The Weather and its elements is one of the most common topics of conversation and an essential part of our daily lives. It affects how we dress, what activities we can do, and even our moods. Despite being such a familiar subject, the concept of weather encompasses a variety of phenomena and complexities that shape the environment around us. This article explores weather in its many forms, its causes, and its significance in everyday life.
What Is Weather?
The state of the atmosphere at a certain location and time is referred to as the weather. It includes conditions such as temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure. Unlike climate, which describes long-term patterns, weather is all about short-term variations that can change within minutes or hours.

Components of Weather
Several elements come together to create the weather we experience. These include:
- The air’s temperature indicates how hot or cold it feels. It is measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F) and is influenced by factors such as the sun’s energy, geographical location, and altitude.
- The quantity of water vapor in the air is referred to as humidity. High humidity often makes the air feel sticky and uncomfortable, while low humidity can make it feel dry.
- Precipitation: This includes rain, snow, sleet, or hail. Precipitation occurs when water vapor in the atmosphere cools and condenses into droplets or ice crystals, which then fall to the ground.
- Wind: The movement of air due to variations in atmospheric pressure is called wind. It can range from a gentle breeze to strong gusts and plays a role in spreading heat and moisture.
- Atmospheric Pressure: This is the weight of the air above us. Changes in pressure can signal shifts in the weather, such as the arrival of a storm.
What Causes Weather?
The primary driver of weather is the sun. Solar energy heats the Earth’s surface unevenly due to its tilt and rotation, leading to variations in temperature. These temperature differences create pressure differences in the atmosphere, causing air to move. This movement of air, along with the Earth’s rotation, generates wind patterns and weather systems.

Other factors influencing weather include:
- The Water Cycle: The continuous movement of water between the Earth and atmosphere plays a vital role in weather patterns. Processes like evaporation, condensation, and precipitation are integral to this cycle.
- Geography: Mountains, oceans, and forests can significantly influence weather. For example, coastal areas often experience milder temperatures, while mountains can block or redirect air currents.
- Seasons: The Earth’s tilt causes changes in sunlight throughout the year, leading to seasonal variations in weather.
Types of Weather
Weather can take many forms, from sunny and clear days to extreme conditions. Here are some common types:
- Sunny: Clear skies and bright sunlight, often associated with high temperatures.
- Cloudy: Overcast skies, which can range from light cloud cover to complete grayness.
- Rainy: Frequent precipitation, which can vary in intensity from light drizzle to heavy downpours.
- Snowy: Cold weather conditions where snow falls instead of rain.
- Stormy: Intense weather with strong winds, thunder, lightning, and sometimes heavy rain.
- Foggy: Low visibility caused by condensed water vapor near the ground.
How Weather Impacts Daily Life

Weather affects nearly every aspect of our lives. From the clothes we wear to the activities we plan, it plays a central role. Here are some examples of how weather impacts us:
- Transportation: Snow, rain, or fog can disrupt travel, leading to delays or hazardous conditions.
- Health: Extreme weather, such as heatwaves or cold snaps, can pose risks to health, particularly for vulnerable populations.
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on specific weather conditions for planting and harvesting crops. Droughts or excessive rainfall can significantly impact food production.
- Recreation: Outdoor activities are often dependent on favorable weather conditions, whether it’s sunny skies for a picnic or snow for skiing.
Weather Forecasting
Advances in technology have made weather forecasting more accurate than ever. Meteorologists use tools like satellites, radar, and weather stations to collect data on atmospheric conditions. This data is analyzed using computer models to predict future weather patterns. While forecasts are not always perfect, they provide valuable information for planning and preparedness.
Extreme Weather Events
Occasionally, weather can become extreme and pose significant challenges. Examples include:
- Hurricanes: Powerful storms with strong winds and heavy rainfall, typically forming over warm ocean waters.
- Tornadoes: Rotating columns of air that extend from thunderstorms to the ground, capable of causing widespread damage.
- Floods: Excessive rainfall or rapid snowmelt can lead to water overflowing onto land.
- Heatwaves: Extended periods of extremely high temperatures that can be dangerous to health.
- Severe snowstorms with high winds and poor visibility are known as blizzards.
The Importance of Weather Awareness
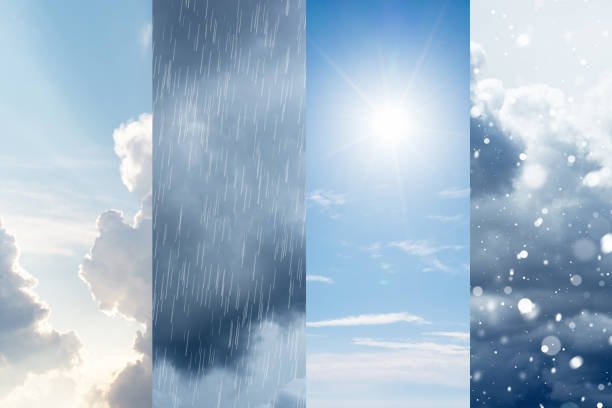

Understanding weather and staying informed about forecasts can help us prepare for different conditions. It allows us to:
- Plan activities and events accordingly.
- Take precautions during extreme weather to ensure safety.
- Support efforts to mitigate the impact of adverse weather on vulnerable communities.
Conclusion
Weather is a dynamic and fascinating aspect of our environment. While it can be unpredictable and challenging at times, it also brings beauty and variety to our lives. By understanding the basics of weather, we can better appreciate its influence and be prepared to adapt to its changes. Whether it’s a sunny day or a stormy night, weather continues to shape our world in countless ways.